ARRAYS
An array is a collection of data that holds fixed number of values of same type. For example: if you want to store marks of 100 students, you can create an array for it.
float marks[100] ;
The size and type of arrays cannot be changed after its declaration.
Arrays are of two types:
- One-dimensional arrays
- Multi dimensional arrays
How to declare an array in C?
data_type array_name[array_size];
For example,
float mark[5];
Here, we declared an array, mark, of floating-point type and size 5. Meaning, it can hold 5 floating-point values.
Elements of an Array and How to access them?
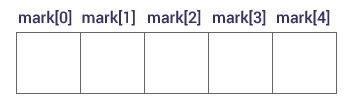
You can access elements of an array by indices.
Suppose you declared an array mark as above. The first element is mark[0], second element is mark[1] and so on.
Few key notes:
- Arrays have 0 as the first index not 1. In this example, mark[0]
- If the size of an array is n, to access the last element,
(n-1)index is used. In this example, mark[4] - Suppose the starting address of
mark[0]is 2120d. Then, the next address,a[1], will be 2124d, address ofa[2]will be 2128d and so on. It's because the size of a float is 4 bytes.
How to initialize an array in C programming?
It's possible to initialize an array during declaration. For example,
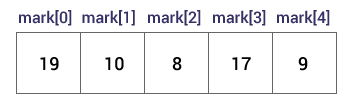
int mark[5] = {19, 10, 8, 17, 9};
Another method to initialize array during declaration:
int mark[] = {19, 10, 8, 17, 9};
Here,
mark[0] is equal to 19
mark[1] is equal to 10
mark[2] is equal to 8
mark[3] is equal to 17
mark[4] is equal to 9
How to insert and print array elements?
int mark[5] = {19, 10, 8, 17, 9}
// take input from the user and insert in third element
scanf("%d", &mark[2]);
// take input from the user and insert in (i+1)th element
scanf("%d", &mark[i]);
// print first element of an array
printf("%d", mark[0]);
// print ith element of an array
printf("%d", mark[i-1]);
1.Write a program to find the average of n numbers using arrays
/*******************************************************************/
//******************************************************************
# include < stdio.h >
# include < conio.h >
int main ( )
{
int marks[10] , i ,n, sum = 0,average ;
clrscr ( ) ;
Printf ( “ enter n \ n ” ) ;
Scanf ( ” % d ”, &n );
For ( i = 1 ; i < = n ; + + i )
{
Printf ( “ enter number % d \ n ” , i + 1 ) ;
Scanf ( ” % d ”, &marks [ i ] );
sum = sum + marks [ i ] ;
}
average = sum / n ;
Printf ( “ average = % d ” , average ) ;
return 0 ;
}
2.How to pass arrays to a function in C Programming?
n C programming, a single array element or an entire array can be passed to a function.
This can be done for both one-dimensional array or a multi-dimensional array.
Passing One-dimensional Array In Function
Single element of an array can be passed in similar manner as passing variable to a function.
2. C program to pass a single element of an array to function
/*******************************************************************/
//******************************************************************
# include < stdio.h >
# include < conio.h >
void display ( int age )
{
Printf ( ” % d ”, age ) ;
}
int main ( )
{
int agearray [ ] = { 2 , 3 , 4 } ;
clrscr ( ) ;
display ( agearray [ 2 ] ) ;
return 0 ;
}
Passing an entire one-dimensional array to a function
While passing arrays as arguments to the function, only the name of the array is passed (,i.e, starting address of memory area is passed as argument).
3. C program to pass an array containing age of person to a function. This function should find average age and display the average age in main function.
/*******************************************************************/
//******************************************************************
# include < stdio.h >
# include < conio.h >
int average ( int age [ ] ) ;
int main ( )
{
int avg , age [ ] = { 23 , 55 , 66 , 50 , 45 , 25 } ;
clrscr ( ) ;
avg = average ( age ) ;
Printf ( ” average age = % d ”, avg ) ;
return 0 ;
}
int avgerage ( int age[ ] )
{
int i ;
int avg , sum = 0 ;
For ( i = 0 ; i < 6 ; + + i )
{
sum = sum + age [ i ] ;
}
avg = sum / 6 ;
return avg ;
}
Multidimensional Arrays
In C programming, you can create an array of arrays known as multidimensional array. For example,
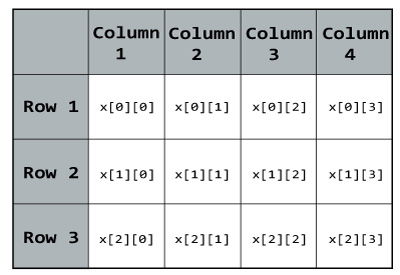
float x [ 3 ] [ 4 ] ;
Here, x is a two-dimensional (2d) array. The array can hold 12 elements. You can think the array as table with 3 row and each row has 4 column.
Similarly, you can declare a three-dimensional (3d) array. For example,
float y [ 2 ] [ 4 ] [ 3 ] ;
Here,The array y can hold 24 elements.
You can think this example as: Each 2 elements have 4 elements, which makes 8 elements and each 8 elements can have 3 elements. Hence, the total number of elements is 24.
How to initialize a multidimensional array?
There is more than one way to initialize a multidimensional array.
Initialization of a two dimensional array
// Different ways to initialize two dimensional array
int c [ 2 ] [ 3 ] = { { 1, 3, 0 } , { -1, 5, 9 } } ;
int c [ ] [ 3 ] = { { 1 , 3 , 0 } , { -1 , 5, 9 } } ;
int c [ 2 ] [ 3 ] = { 1 , 3 , 0 , -1, 5 , 9 } ;
Above code are three different ways to initialize a two dimensional arrays.
Initialization of a three dimensional array.
You can initialize a three dimensional array in a similar way like a two dimensional array. Here's an example,
int test [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] = {
{ {3, 4, 2, 3}, {0, -3, 9, 11}, {23, 12, 23, 2} },
{ {13, 4, 56, 3}, {5, 9, 3, 5}, {3, 1, 4, 9} }
} ;
sum of two matrices using two dimensional arrays
1. C program to find the sum of two matrices of order 2*2 using multidimensional arrays.
/*******************************************************************/
//******************************************************************
# include < stdio.h >
# include < conio.h >
int main ( )
{
int a [ 2 ] [ 2 ] , b [ 2 ] [ 2 ] , c [ 2 ] [ 2 ] , i , j ;
clrscr ( ) ;
// Taking input using nested for loop
Printf ( “ enter elements of 1st matrix \ n ” ) ;
For ( i = 0 ; i < 2 ; + + i )
For ( j = 0 ; j < 2 ; + + j )
{
Printf ( ” enter a % d % d : ”, i + 1 , j + 1 ) ;
Scanf ( ” % d ”, &a [ i ] [ j ] ) ;
}
// Taking input using nested for loop
Printf ( “ enter elements of 2nd matrix \ n ” ) ;
For ( i = 0 ; i < 2 ; + + i )
For ( j = 0 ; j < 2 ; + + j )
{
Printf ( ” enter b % d % d : ”, i + 1 , j + 1 ) ;
Scanf ( ” % d ”, &b [ i ] [ j ] ) ;
}
// adding corresponding elements of two arrays
For ( i = 0 ; i < 2 ; + + i )
For ( j = 0 ; j < 2 ; + + j )
{
c [ i ] [ j ] = a [ i ] [ j ] + b [ i ] [ j ] ;
}
// Displaying the sum
Printf ( “ sum of matrix \ n ” ) ;
For ( i = 0 ; i < 2 ; + + i )
For ( j = 0 ; j < 2 ; + + j )
{
Printf ( " % d \ t " , c [ i ] [ j ] ) ;
if ( j = = 1 )
Printf ( " \ n " ) ;
}
return 0 ;
}
2. Program to Find Transpose of a Matrix
/*******************************************************************/
//******************************************************************
# include < stdio.h >
# include < conio.h >
int main ( )
{
int a [ 10 ] [ 10 ] , transpose [ 10 ] [ 10 ] , r , c , i , j ;
clrscr ( ) ;
Printf ( “ enter rows and columns of a matrix \ n ” ) ;
scanf ( " % d % d " , & r, & c ) ;
// Storing elements of the matrix
For ( j = 0 ; j < c ; + + j )
{
Printf ( " Enter element a % d % d : " , i + 1 , j + 1 ) ;
Scanf ( " % d " , &a [ i ] [ j ] ) ;
}
/ / Displaying the matrix a [ ] [ ]
Printf ( " \ n Entered Matrix : \ n " ) ;
For ( j = 0 ; j < c ; + + j )
Printf ( " % d ", a [ i ] [ j ] ) ;
if ( j = = c - 1 )
Printf ( " \ n \ n " ) ;
}
// Finding the transpose of matrix a [ ] [ ]
For ( j = 0 ; j < c ; + + j )
transpose [ j ] [ i ] = a [ i ] [ j ] ;
}
// Displaying the transpose of matrix a [ ] [ ]
Printf ( " \ n Transpose of Matrix : \ n " ) ;
For ( j = 0 ; j < r ; + + j )
Printf ( " % d " , transpose [ i ] [ j ] ) ;
if ( j = = r - 1 )
Printf ( " \ n \ n " ) ;
}
return 0;
}
